Thank you Kristian for this excellent video and your friendly support!
All posts by david
From DS8 to DM77
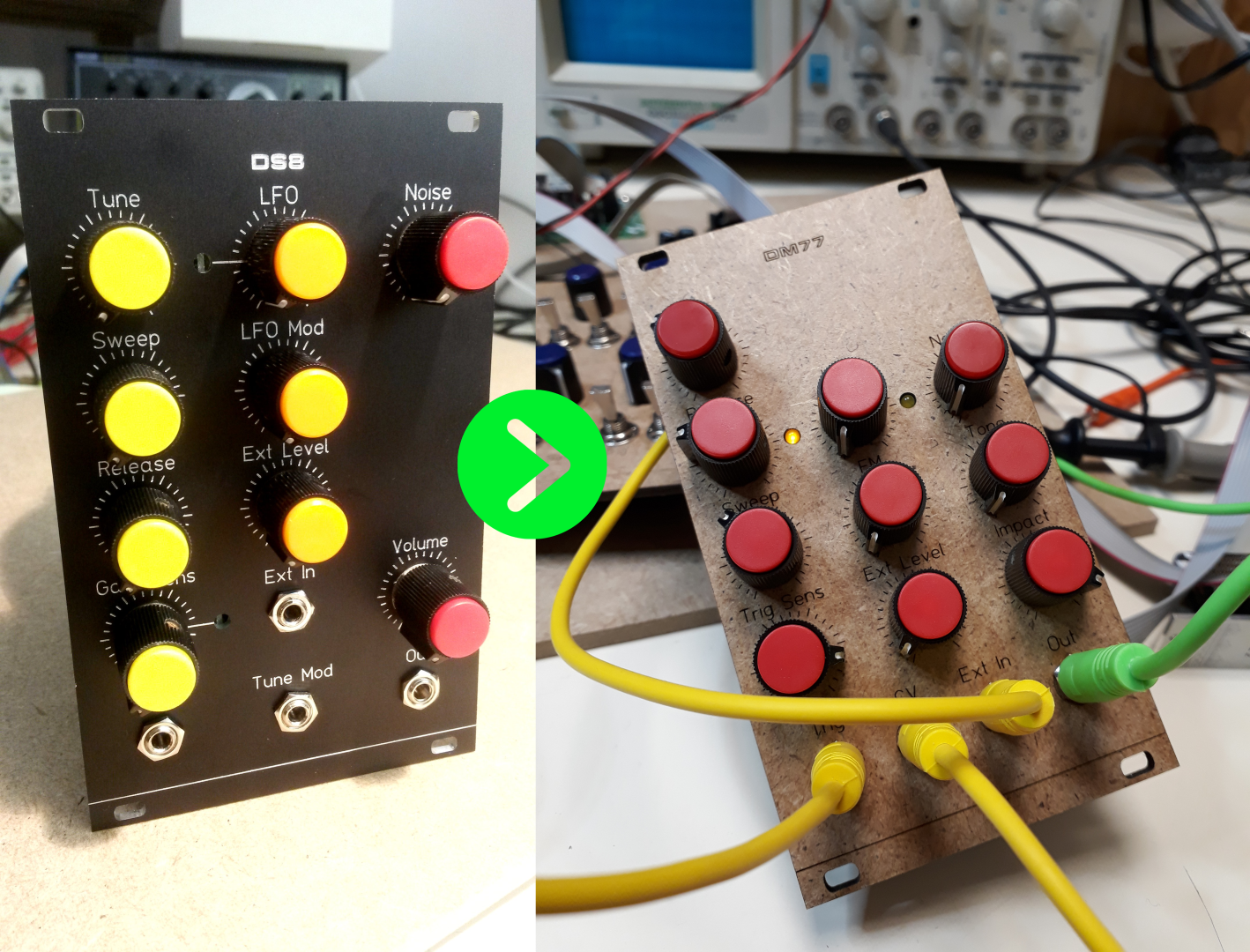

One of my first projects (and one of my first posts here) was about a clone of the classic funky/cheesy drum synth, the Coron DS8. You know the piouuu piouuu drum sounds from disco era? Well it’s probably the DS8.
Continue reading From DS8 to DM77
MFOS SLMS – Demo
A short demo of the SLMS, showing the following features: CV input, Low Pass filter with resonance, VCA, Gate input, Attack/Release with retrig and LFO.
The CV and Gate signals are generated by MIDI interface CVpal by Mutable Instruments. The sequence is generated by Qtractor on Linux.
Recorded with my Tascam DR-08.
Laser cut MDF Euro Panels for the Sound Lab Mini-Synth
I’m having fun at my local Fablab!
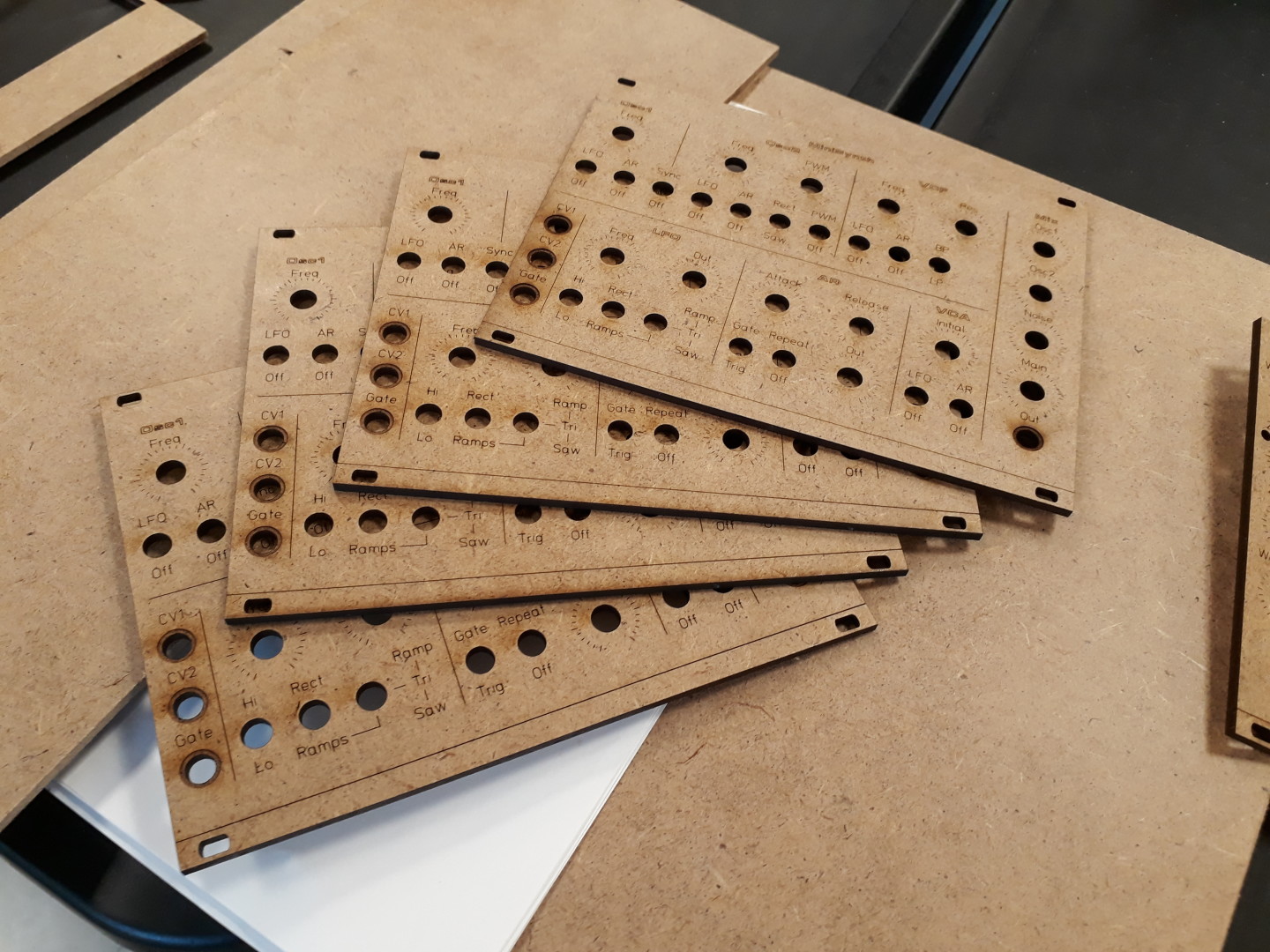

Continue reading Laser cut MDF Euro Panels for the Sound Lab Mini-Synth
MFOS WSG – Demo
A quick and dirty demo on the capabilities of the WSG. Warning, lot of sounds.
MFOS Weird Sound Generator in SMT
The SMT adaptation was a hobby project. The MFOS designs are the property of SynthCube.
If you want to buy PCB for the MFOS synths, please visit musicfromouterspace.com
Here comes my next conversion of Ray’s classic analog synthesizer, the Weird Sound Generator!
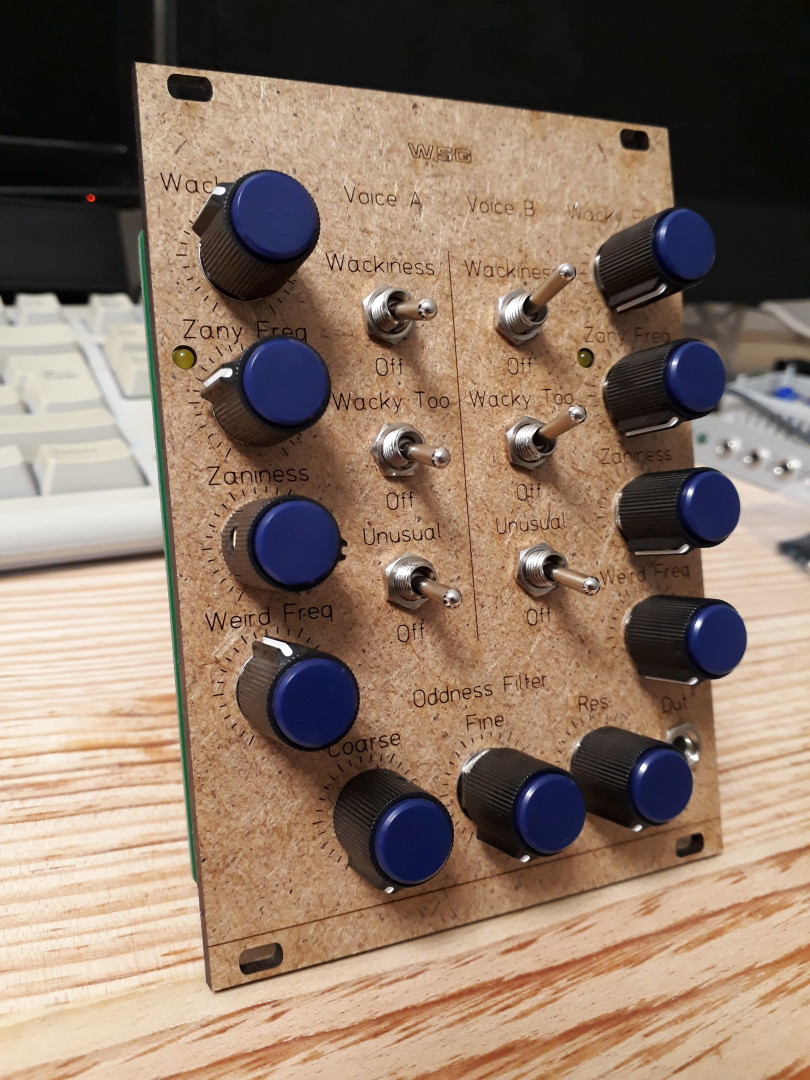

This is the same process as for my previous SMT/Eurorack conversion of the Sound Lab Mini-Synth. The circuit is identical to the original, including component references.
MFOS Sound Lab Mini-Synth in SMT – Assembly Instructions – v1.2
The SMT adaptation was a hobby project. The MFOS designs are the property of SynthCube.
If you want to buy PCB for the MFOS synths, please visit musicfromouterspace.com
MFOS Sound Lab Mini-Synth is a cool analog monophonic synthesizer. The original version has been created by Ray Wilson from Music From Outer Space.
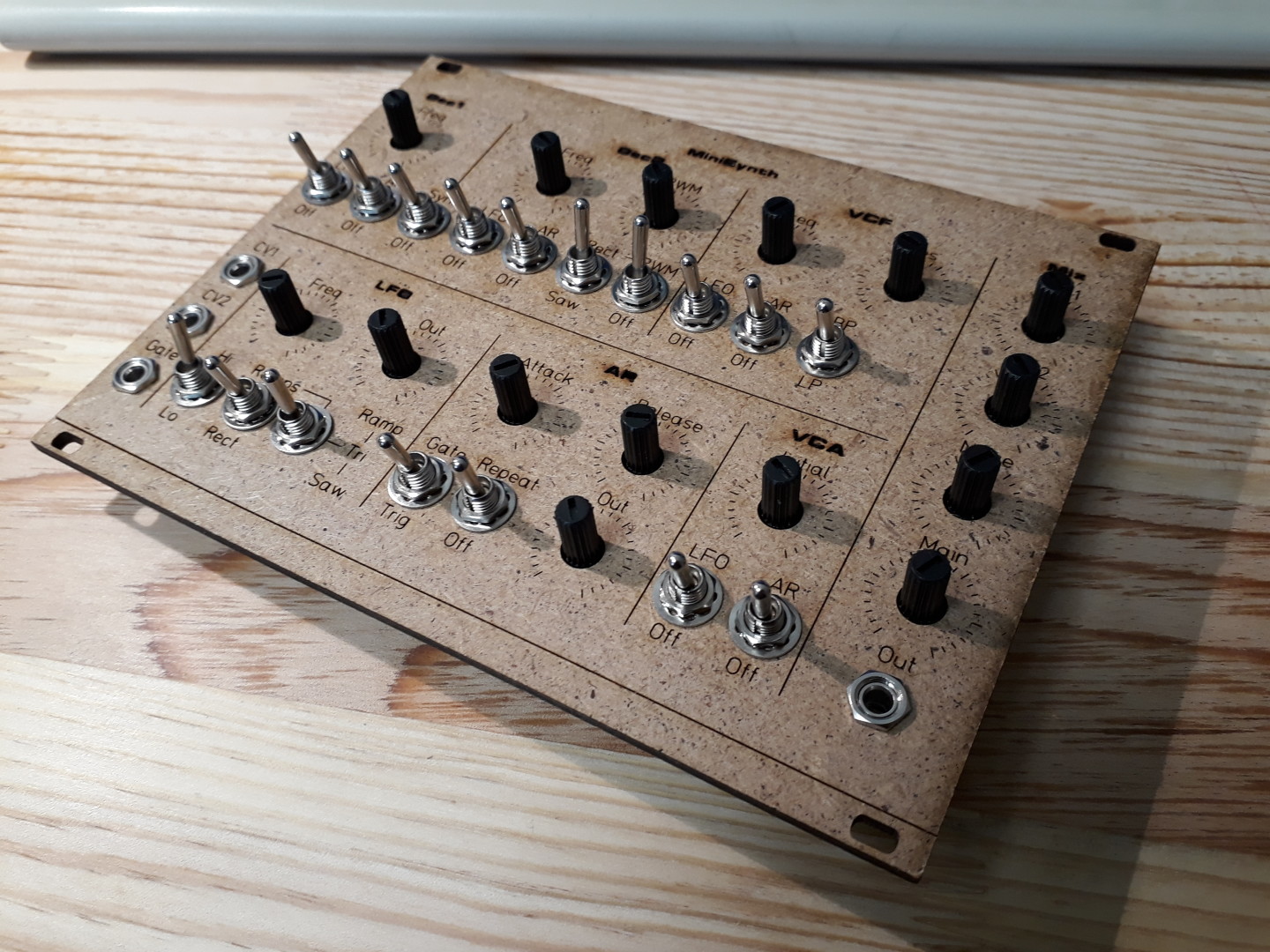

Continue reading MFOS Sound Lab Mini-Synth in SMT – Assembly Instructions – v1.2
KiCad 3D Library – 9mm Alpha/Alps Potentiometers
I keep creating new 3D models for KiCad. This time I made some 9mm potentiometers I use in all my projects.
ALPHA / ALPS 9mm single turn Potentiometers:
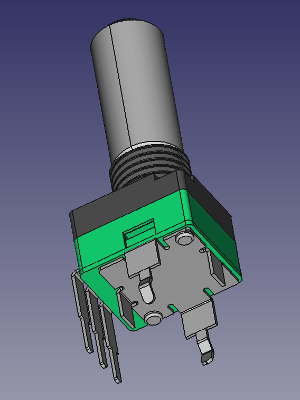
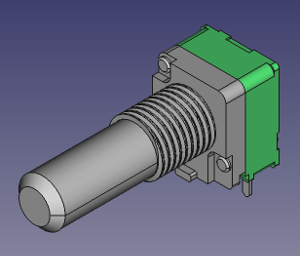
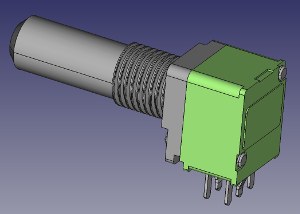
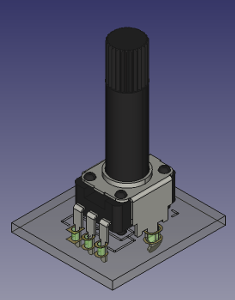
Download on Github : https://github.com/dhaillant/kicad-3dmodels/tree/master/potentiometers
MFOS SoundLab MiniSynth in SMT – 1.2 Update
The SMT adaptation was a hobby project. The MFOS designs are the property of SynthCube.
If you want to buy PCB for the MFOS synths, please visit musicfromouterspace.com
This is an updated version of my SMT conversion of MFOS SoundLab MiniSynth!
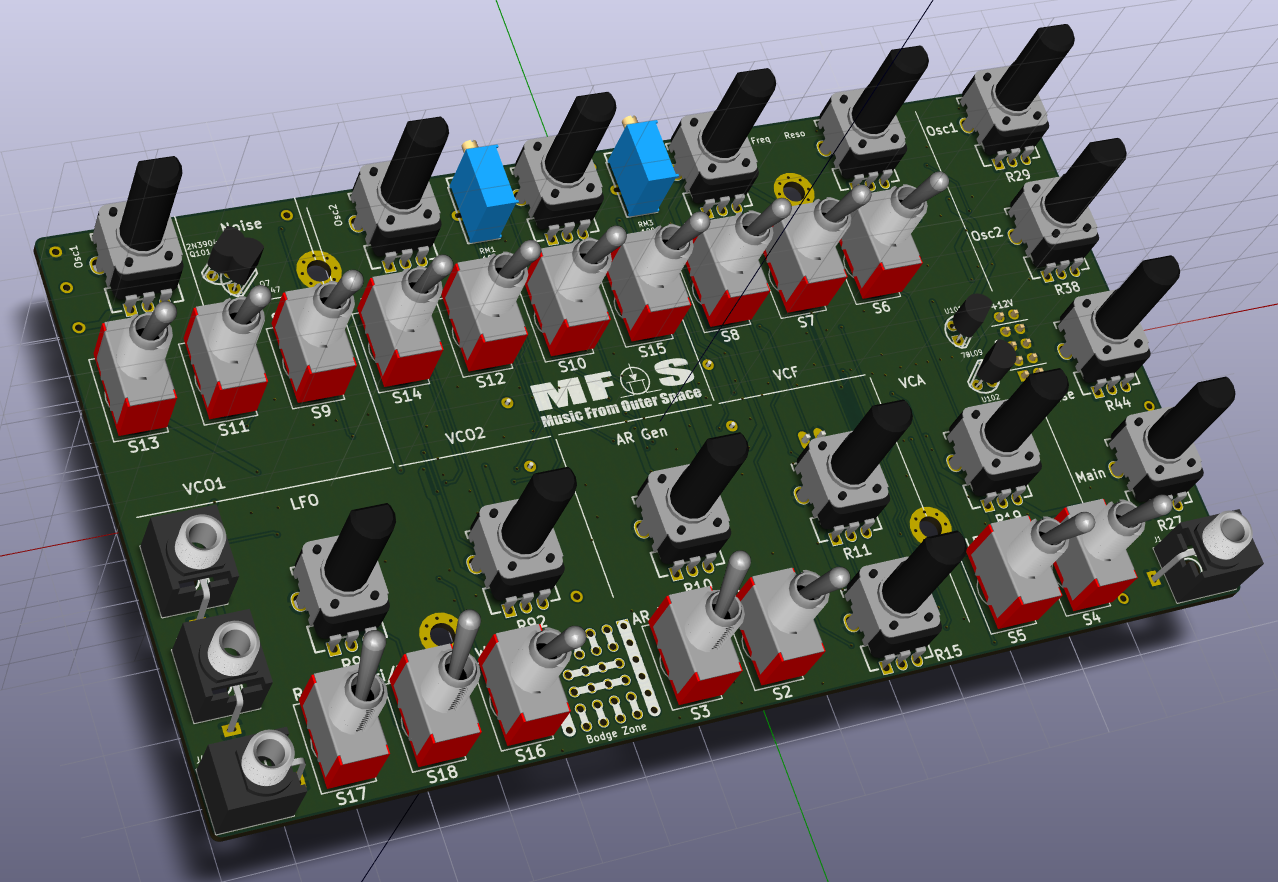
Continue reading MFOS SoundLab MiniSynth in SMT – 1.2 Update
KiCad 3D Library – BOURNS-3296
I’m updating all my current designs in order to incorporate WRL/STEP 3D models. They provide a convenient way to check mechanical issues, especially with cases and front panels.
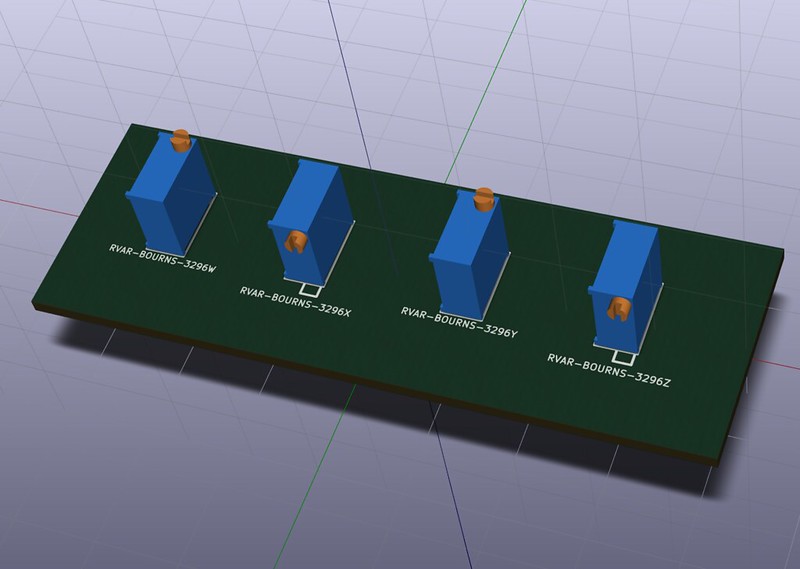
The Bourns 3296 3/8″ Trimpots are missing from the official KiCad 3D Library, so I decided to create my own.
It’s also a useful way to learn how to use FreeCAD and Github.
I’m also using kicad StepUp for model conversion, alignement and scaling.
You can find my 3D lib on GitHub here: https://github.com/dhaillant/kicad-3dmodels